1 Introduction
Data science is an exciting discipline that allows you to turn raw data into understanding, insight, and knowledge. The goal of “R for Data Science” is to help you learn the most important tools in R that will allow you to do data science. After reading this book, you’ll have the tools to tackle a wide variety of data science challenges, using the best parts of R.
Data Science Project process:
Data science is a huge field, and there’s no way you can master it by reading a single book. The goal of this book is to give you a solid foundation in the most important tools. Our model of the tools needed in a typical data science project looks something like this:
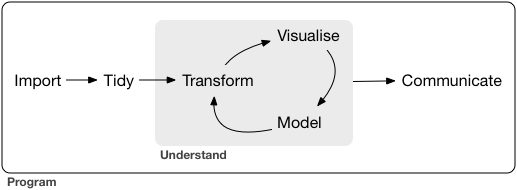
What you won’t learn
- Big Data
- Python, Julia, and friends
- Non-rectangular data
- Hypothesis confirmation
Prerequisites
R
- Download R from CRAN: https://cran.r-project.org
- Cloud mirror: https://cloud.r-project.org (which automatically figures it out for you.)
RStudio
- Download and install it from http://www.rstudio.com/download
- RStudio IDE Cheat Sheet: https://www.rstudio.com/resources/cheatsheets/#ide
The tidyverse packages
Install the tidyverse packages:
if (!require("tidyverse")) install.packages("tidyverse")Load it with the library() function:
library(tidyverse)
## Registered S3 methods overwritten by 'ggplot2':
## method from
## [.quosures rlang
## c.quosures rlang
## print.quosures rlang
## ── Attaching packages ────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.2.1 ──
## ✔ ggplot2 3.1.1 ✔ purrr 0.3.2
## ✔ tibble 2.1.1 ✔ dplyr 0.8.1
## ✔ tidyr 0.8.3 ✔ stringr 1.4.0
## ✔ readr 1.3.1 ✔ forcats 0.4.0
## ── Conflicts ───────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
## ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()Update the packages:
tidyverse_update()Other packages
In this book we’ll use three data packages from outside the tidyverse:
install.packages(c("nycflights13", "gapminder", "Lahman"))